1.2m collimator for the Euclid space telescope
Euclid is an ESA mission to map the geometry of the dark Universe. The mission will investigate the distance-redshift relationship and the evolution of cosmic structures by measuring shapes and redshifts of galaxies and clusters of galaxies out to redshifts ~2, or equivalently to a look-back time of 10 billion years.
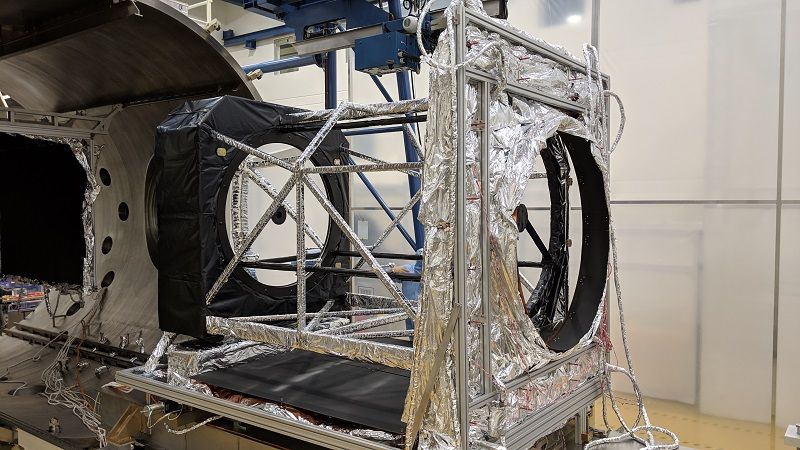
The Euclid space probe is based on a 1m infrared telescope. This cutting-edge instrument needed to be tested in representative thermal and vacuum conditions. For this purpose, AMOS was contracted the building of a 1.2m collimator designed to project to the telescope a signal that would look as if coming from the infinity of the universe.
Despite the fact that the collimator has a precision better than the instrument it measures, it is also placed in te same thermal-vacuum chamber than the telescope. It was thus designed to be able to test the telescope in vacuum, at a temperature of 100°K.
This resulted in a complex collimator design, with active thermal control and very tight specifications, especially regarding the line-of-sight accuracy.

The whole space telescope and the collimator were tested together in CSL, in the FOCAL-V vacuum chamber, also built by AMOS.
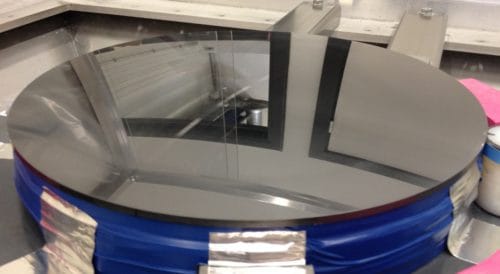
The EUCLID collimator integrates a zerodur 1.2m mirror and a Silicon Carbide secondary mirror in a mixed aluminum and steel structure.
 info@amos.be
info@amos.be
 +32 4 361 40 40
+32 4 361 40 40



 see all
Projects
see all
Projects